Search for a Bariatric Surgeon
SearchInformation Sessions
Information SessionsSchedule an Appointment
ScheduleThinking About Bariatric Surgery? Let Us Help
Get Started on the Path to Bariatric Surgery
Get StartedRefer a Patient
ReferDuodenal Switch
The duodenal switch is a weight loss operation that has been done for over 20 years, and has become more common in the last several years. It has the greatest weight loss potential of all the available operations.
Highlights
- Greatest weight loss potential of all bariatric procedures
- Minimal risk of dumping syndrome
- Excellent diabetes control
- Minimal risk of ulcer disease
What to Expect
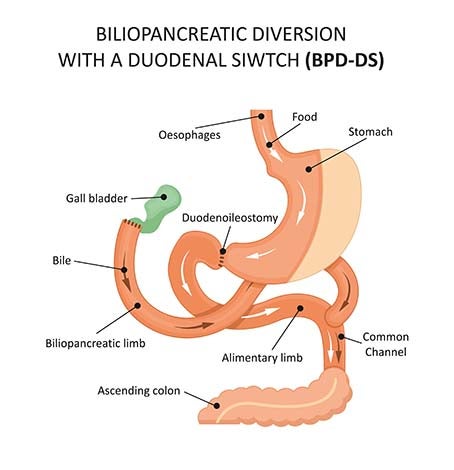
The duodenal switch works by creating a sleeve gastrectomy for restriction and hunger control. Then, after the sleeve, the intestines are rerouted similar to a gastric bypass.
The principle measured length with a duodenal switch is the common channel. This is the distance from where bile and food meets to the end of the small intestines and determines the amount of malabsorption.
The common channel distance is important and can vary based on individual patients. We typically create a 300 cm common channel. Vitamin supplementation is important and patients may have some increase in the number of bowel movements.
First, the sleeve is created with a surgical stapler along the outside curve of the stomach. After the new stomach is created, the excess stomach is removed. The valve at the outlet of the stomach remains, which allows for the normal process of stomach-emptying and the feeling of fullness. The small intestine is carefully counted from the base of the large intestine, then is divided and reconfigured to allow for decreased absorption.
Surgery takes about an hour and a half and patients have a similar recovery to other bariatric procedures. Food enters the sleeve and is held there with the pylorus just like a sleeve. Because of this, dumping syndrome does not occur, unlike the gastric bypass.
Results
Patients can expect to lose 80 to 90 percent of excess weight in the first year after a duodenal switch operation. Results vary by patient.
Disadvantages
Specific disadvantages include:
- Greater risk for nutritional and fluid deficiencies (must be on life long vitamins)
- Gastric reflux
Potential Concerns
In addition to standard surgical risks, concerns to be aware of include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Leaks from staple line
- Gastric reflux
- Small bowel obstruction
- Increased risk of reflux disease
- Greater risk of nutrition deficiencies if patient isn’t compliant with recommendations
What to Expect After Surgery
A hospital stay after a duodenal switch procedure is typically 24 to 48 hours. Many patients return to normal activity within one to two weeks. Heavy lifting is restricted for about four weeks.