Spinal Cord Injuries
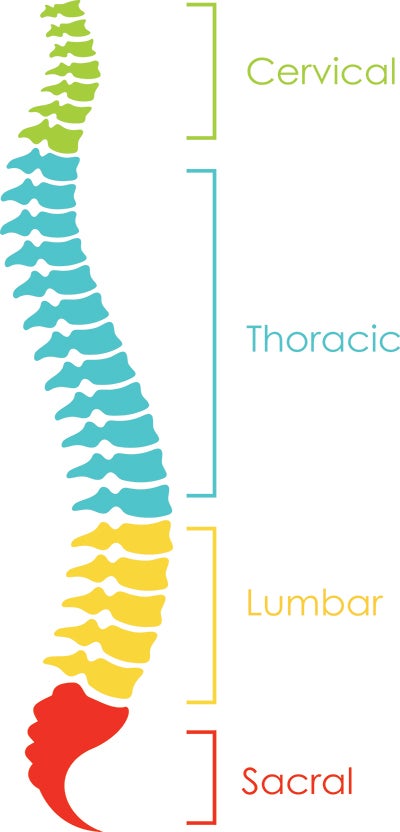 What is a Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)?
What is a Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)?
- A spinal cord injury is damage to the cells and nerves that send and receive signals from the brain to and from the rest of the body.
- Some injuries cause little or no damage to the spinal cord nerves and can allow for an almost complete recovery of function over time.
- More serious injuries can cause long-term deficits, such as paralysis — or loss of strength, sensation and body function in certain parts of the body.
- The part of the spinal cord that is damaged determines what parts of your body are most affected by the injury.
Common Causes of SCI
- Car accidents
- Sports-related injuries
- Violence or assault
- Falls Definitions
- Paraplegia — full or partial paralysis of the lower half of the body
- Quadriplegia — paralysis of both legs and both arms
Common Symptoms of SCI
- Paraesthesia (numbness, tingling or a loss of or changes in sensation) in the hands and feet.
- Pain or pressure in your neck, head or back.
- Paralysis that may occur immediately or over time.
- Loss of voluntary or involuntary movement that can result in trouble breathing, loss of bladder and bowel control and walking.
- Changes in sexual function. Ask your provider or care team if you are experiencing any of these symptoms or if you have any questions.
How to Diagnose A SCI
In an emergency, a physician may be able to rule out a SCI with examination of the head, neck and back, asking questions and testing for sensory function, movement, pain and the ability to breath.
Tests to diagnose SCI may include:
- X-ray
- CT scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
When some of the swelling from a SCI has decreased, a physician will conduct more neurological tests to determine the location and severity of the injury.
How to Treat A SCI
Current treatment focuses on:
- Maintaining a person’s ability to breathe, if needed
- Immobilization to prevent further injury
- Surgery to remove fragments of bone or other objects that may be compressing the spine, fixing fractures and stabilizing the spine.
- Rehabilitation to strengthen muscle function and learning adaptive techniques to complete daily activities.
At WakeMed, patients with SCI will be typically admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) and will have a specialized team including nurses; providers; and physical, occupational and respiratory therapists who evaluate them to provide the best care possible.
Some resources for you to explore:
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke | (800) 352-9424
- Academy of Neurologic Physical Therapy | (952) 646-2038
- Unite 2 Fight Paralysis | (888) 564-2228
- North Carolina SCI Association (NCSCIA) and for support groups in your area
Information and images adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke